M270 PFAS Treatment for Industrial Water Systems
M270 PFAS Treatment for Industrial Water Systems
Blog Article
Advanced Approaches for Reliable PFAS Contamination Removal
The persistent challenge of PFAS contamination necessitates the exploration of sophisticated elimination approaches that can efficiently address these dangerous compounds. Cutting-edge innovations, such as sophisticated oxidation procedures and numerous adsorption methods, have actually arised as promising remedies in mitigating PFAS from affected settings.
Comprehending PFAS Residences
Although per- and polyfluoroalkyl compounds (PFAS) have actually been commonly made use of in different commercial and customer products due to their unique buildings, their persistence in the environment poses significant difficulties to public health and safety. PFAS are a team of synthetic chemicals defined by a carbon-fluorine bond, among the strongest chemical bonds recognized, which adds to their exceptional stability and resistance to degradation. This stability enables PFAS to collect in the environment and living microorganisms, resulting in potential adverse health and wellness effects.
The hydrophobic and oleophobic nature of PFAS makes them particularly reliable in applications such as non-stick finishes, stain-resistant fabrics, and firefighting foams. Nonetheless, these exact same residential or commercial properties add to their environmental determination, as PFAS do not conveniently damage down through all-natural processes. Moreover, their prevalent use has actually caused common contamination of water resources and dirts, complicating removal efforts. Recognizing the chemical homes of PFAS is vital for establishing effective techniques to take care of and minimize their environmental effect. The distinct features of these compounds necessitate a nuanced technique to resolve the challenges positioned by their presence in ecological communities and possible human direct exposure.
Innovative Remediation Technologies
The determination of PFAS in the atmosphere has stimulated the growth of innovative remediation technologies targeted at effectively eliminating these contaminants from impacted ecosystems. Amongst one of the most appealing approaches are innovative oxidation processes (AOPs), which use powerful oxidants to break down PFAS compounds into much less damaging materials. AOPs can be customized to target certain PFAS structures, boosting their efficacy.
An additional arising technology is making use of adsorption media, such as turned on carbon and ion exchange materials, which can uniquely catch PFAS from contaminated water. These materials have revealed considerable elimination efficiencies, although routine substitute and regrowth are essential to preserve efficiency.
Membrane filtration methods, consisting of reverse osmosis and nanofiltration, are likewise obtaining grip in PFAS removal. These approaches can successfully divide PFAS from water, supplying a sensible solution for dealing with polluted sources. Furthermore, thermal treatment approaches, such as incineration, can disintegrate PFAS right into safe results, though they need cautious management to control exhausts.
Jointly, these innovative remediation innovations stand for substantial advancements in the recurring battle against PFAS contamination, supplying numerous techniques to restore damaged atmospheres and safeguard public wellness.
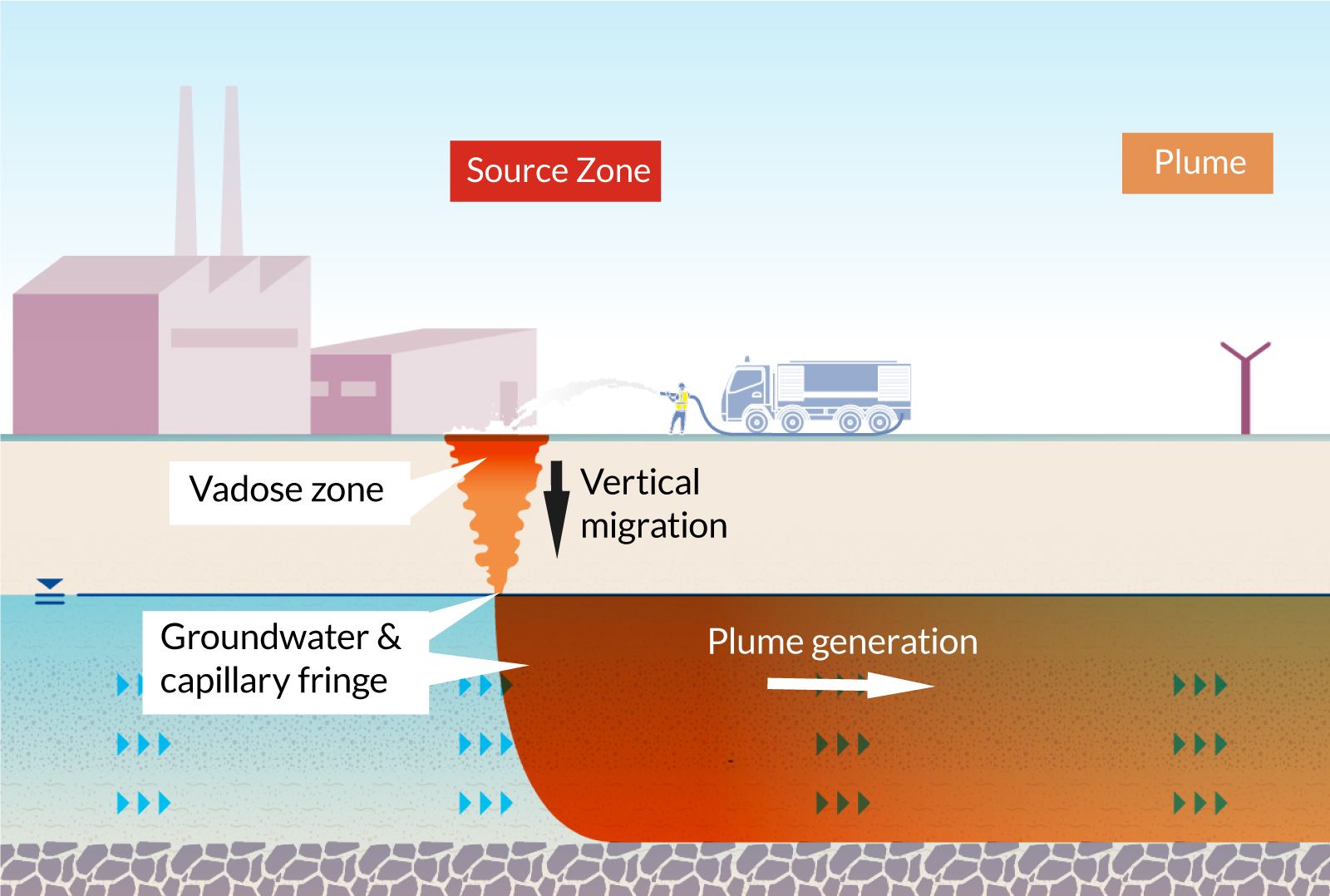
Bioremediation Techniques
Bioremediation methods use an appealing strategy to dealing with PFAS contamination by taking advantage of the all-natural capacities of microorganisms to degrade these persistent substances (m270 waste management). This technique entails the use of bacteria, fungis, and other germs that can metabolize or change PFAS materials right into much less dangerous byproducts
Current advancements in molecular biology and ecological microbiology have improved our understanding of microbial communities and their potential functions in PFAS degradation. Scientists are proactively discovering details pressures of microorganisms, such as Pseudomonas and Bacillus, which have actually shown the ability to break down particular PFAS compounds.
Sitting bioremediation strategies, where bacteria are stimulated straight in contaminated environments, can be specifically efficient. This technique often involves the application of nutrients or electron donors to advertise microbial development and task. Furthermore, ex lover situ techniques, such as bioreactors, permit controlled problems that can optimize degradation rates.
In spite of the guarantee of bioremediation, challenges stay, consisting of the intricate nature of PFAS go right here compounds and the need for extensive area screening - m270 waste management. Continued r & d will be crucial to refine these techniques and analyze their performance in varied ecological contexts
Adsorption and Filtration Methods
Resolving PFAS contamination their explanation frequently involves employing adsorption and filtration methods, which are designed to remove these persistent chemicals from water and dirt. Among the various methods, triggered carbon adsorption is commonly used due to its high area and porosity, enabling effective capturing of PFAS molecules. Granular activated carbon (GAC) systems are specifically preferred for dealing with large quantities of infected water, while powdered activated carbon (POLITICAL ACTION COMMITTEE) can be utilized for smaller-scale applications.
Ion exchange resins also show assurance in PFAS removal, functioning by trading PFAS ions with less unsafe ions in the water. This method has actually demonstrated effectiveness in focusing PFAS compounds, promoting their subsequent elimination. Furthermore, membrane layer filtering strategies, such as reverse osmosis and nanofiltration, run by using semi-permeable membranes to different PFAS from water, properly reducing their concentrations.
While these approaches are reliable, they should be very carefully picked based upon the certain PFAS compounds existing and the environmental context. Continual innovations in materials scientific research and engineering are resulting in the development of novel adsorbents and purification systems that improve removal performances and lower operational prices, consequently improving general remediation initiatives.
Regulatory and Policy Considerations
How can effective regulatory structures boost the management of PFAS contamination? Detailed plans are necessary to ensure a collaborated and robust response to the challenges posed by per- and polyfluoroalkyl materials (PFAS) Regulations can develop clear guidelines for monitoring, reporting, and remediating PFAS-contaminated sites, fostering liability amongst markets and public entities. (m270 waste management)

On top of that, monetary motivations and gives can be integrated right into plans to motivate the fostering of advanced remediation modern technologies. Policymakers should likewise focus on study and development, making sure that arising methods for PFAS removal are verified and implemented efficiently.
In addition, public awareness and interaction are critical elements of any kind of governing strategy, empowering neighborhoods to support for their health and wellness. Inevitably, a well-structured regulatory atmosphere will certainly not only improve the management of PFAS contamination but additionally promote lasting methods that original site secure future generations.
Conclusion
In recap, the complexity of PFAS contamination necessitates the fostering of advanced remediation approaches. Continued research and growth in this area remain critical to resolving the difficulties positioned by PFAS contamination.
Report this page